
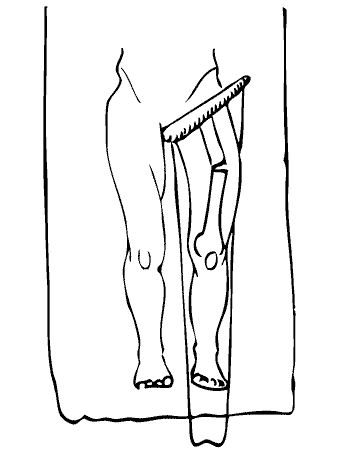
To reduce swelling and relieve pain, your doctor might recommend applying ice packs to the injured area as needed - 15 minutes every three hours. Stay off the affected limb as directed by your doctor until you are cleared to bear normal weight. This may take several months or even longer. It's important to give the bone time to heal.
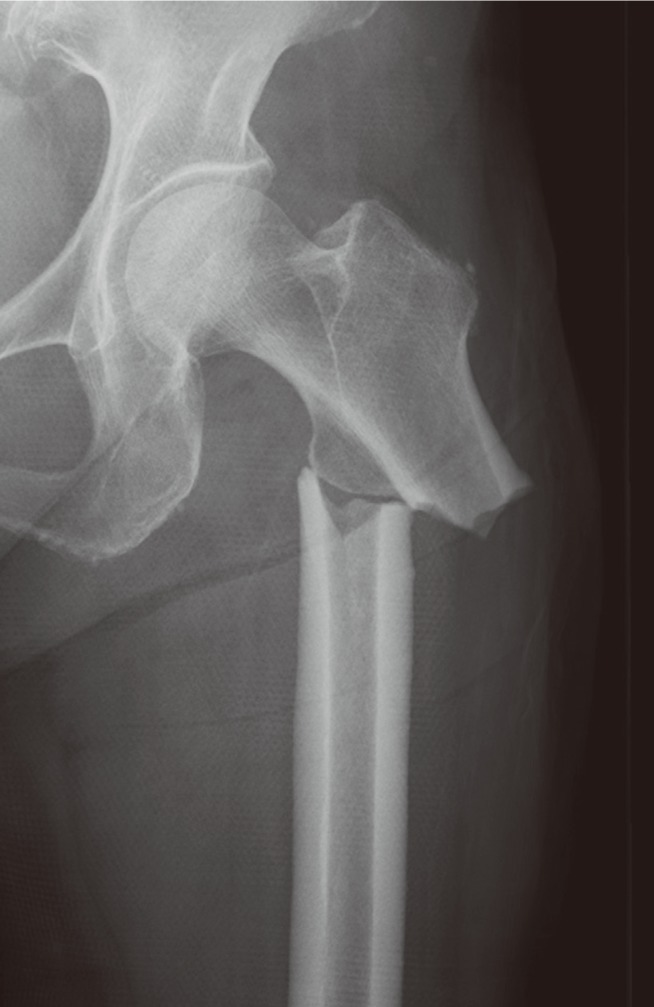
This type of test is also better able to distinguish between stress fractures and soft tissue injuries. It can visualize lower grade stress injuries (stress reactions) before an X-ray shows changes. An MRI is considered the best way to diagnose stress fractures. An MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create detailed images of your bones and soft tissues. However, many types of bone problems look alike on bone scans, so the test isn't specific for stress fractures. The radioactive substance is heavily absorbed by areas where bones are being repaired - showing up on the scan image as a bright white spot. A few hours before a bone scan, you'll receive a small dose of radioactive material through an intravenous line. It can take several weeks - and sometimes longer than a month - for evidence of stress fractures to show on X-rays. Stress fractures often can't be seen on regular X-rays taken shortly after your pain begins. Doctors can sometimes diagnose a stress fracture from a medical history and a physical exam, but imaging tests are often needed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
